M60
Содержание:
Надежность, проблемы и ремонт двигателя БМВ М60Б40
Появившийся в начале 1992 года двигатель V8 серии М60, пришел на смену M30B35 и предназначался для крупных седанов, а также для спортивных купе и закрывал промежуток между рядными шестерками и большими моторами V12. В 60-ю серию входил 3-х литровый M60B30 и наш 4.0 л. M60B40, о котором ниже и пойдет речь.
Блок цилиндров двигателя M60B40 алюминиевый с углом развала 90°, гильзы с никасиловым покрытием и кованым коленвалом. С конца 1994 года, блок заменен на более надежный алюсиловый, поршневая, соответственно, тоже поменялась.Головки блока цилиндров алюминиевые с двумя распределительными валами, по 4 клапана на цилиндр, с гидрокомпенсаторами. Диаметр впускных клапанов 35 мм, выпускных 30.5 мм. Характеристики стандартных распредвалов М60Б40: фаза 246/242, подъем 9.7/9.4 мм.
На М60 использовались индивидуальные катушки зажигания, пластиковый впускной коллектор, двухрядная цепь ГРМ с ресурсом около 200-250 тыс. км. Система управления двигателем Bosch Motronic 3.3.
Данный силовой агрегат использовался на автомобилях BMW с индексом 40i.
В 1996 году двигатель М60В40 был заменен на более совершенный и современный M62B44.
Проблемы и недостатки двигателей BMW M60B40
1. Трясет на холостых. В большинстве случаев проблема решается регулировкой фаз газораспределения. Проверьте еще компрессию, клапан рециркуляции картерных газов и лямбда-зонды.
2. Жор масла. Неисправность решается заменой КВКГ, либо маслосъемных колпачков с кольцами. В случае износа цилиндров спасет гильзовка либо замена блока.
Кроме того, учитывая качество бензина, никасиловые блоки ненадежны, быстро изнашиваются и теряют компрессию, поэтому брать желательно моторы после 94-го года, с алюсиловыми гильзами. Обслуживание двигателя БМВ М60 несколько дороже младшего М50, а также V8 обладает достаточно высоким расходом топлива. К этому стоит добавить возраст двигателей, огромный реальный пробег и активную его эксплуатацию предыдущими владельцами. Учитывая это, к вышеописанным недостаткам добавляются еще и возрастные.
Характеристики M60
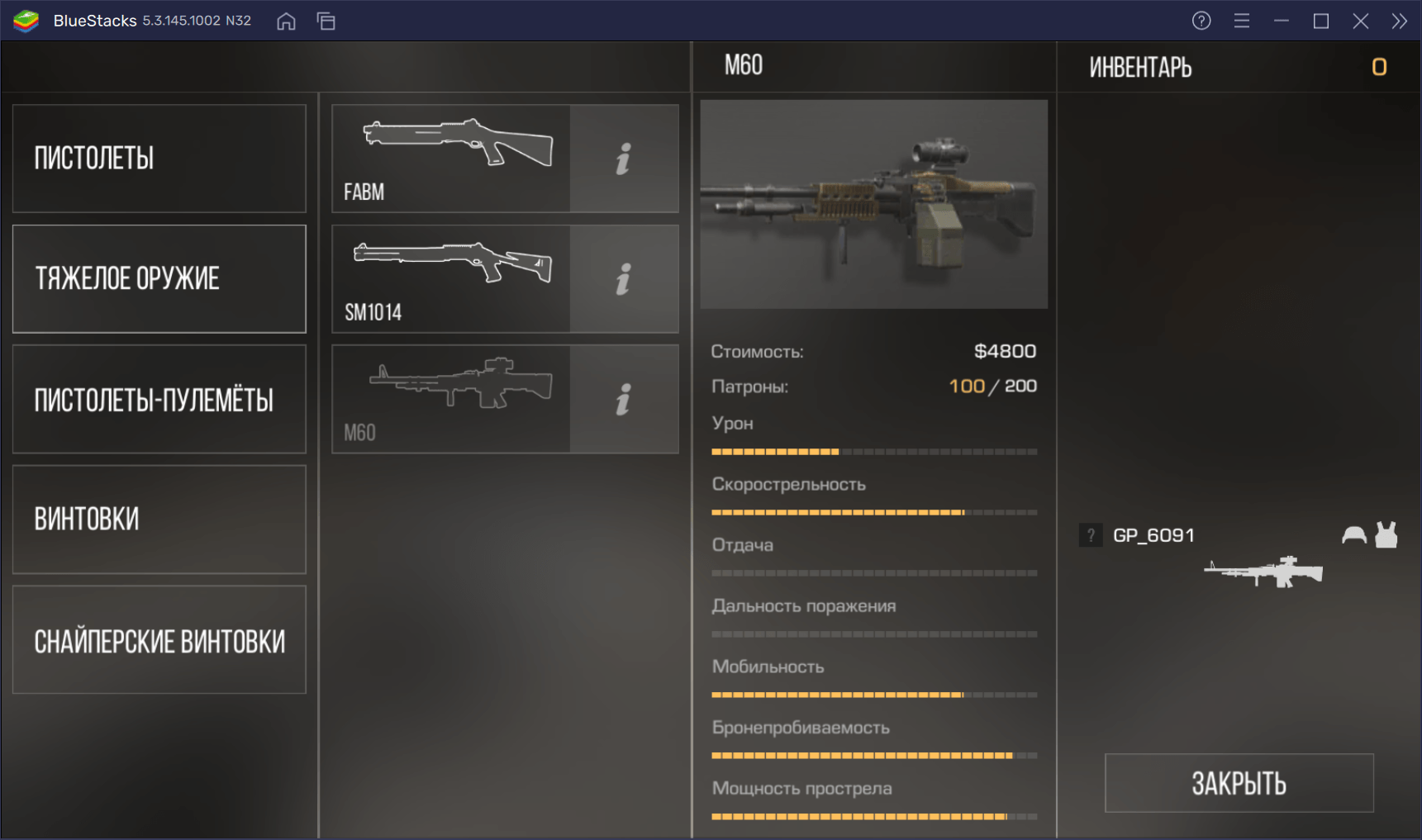
| Урон | 12/30 |
| Скорострельность | 23/30 |
| Отдача | Сильная |
| Дальность поражения | Высокая |
| Мобильность | 23/30 |
| Бронепробиваемость | 28/30 |
| Мощность прострела | 27/30 |
| Количество патронов в обойме | 100 |
| Боезапас патронов | 200 |
| Стоимость | $4800 |
M60 — первый ручной пулемет в Standoff 2. Он был введен в игру, чтобы дать игрокам альтернативу выбора. Его характеристики впечатляют: отличный показатель урона, бронепробиваемость и мощность прострелов. Даже мобильность может показаться хорошей, но… Нет. Поскольку это тяжелый ручной пулемет, персонаж движется с ним очень медленно. Появляется грузность. С непривычки вы можете почувствовать себя неповоротливым и уязвимым.
Выстрелы из M60 убойны. Но чтобы реализовать оружие на 100%, вам нужно научиться контролировать его. За один клик по мыши пулемет выпускает три пули. Их хватит, чтобы свалить даже бронированного противника. Они летят в цель, если вы делаете паузу и даете стволу стабилизироваться. В противном случае его начинает сильно шатать и все пули, кроме первой, уходят мимо.
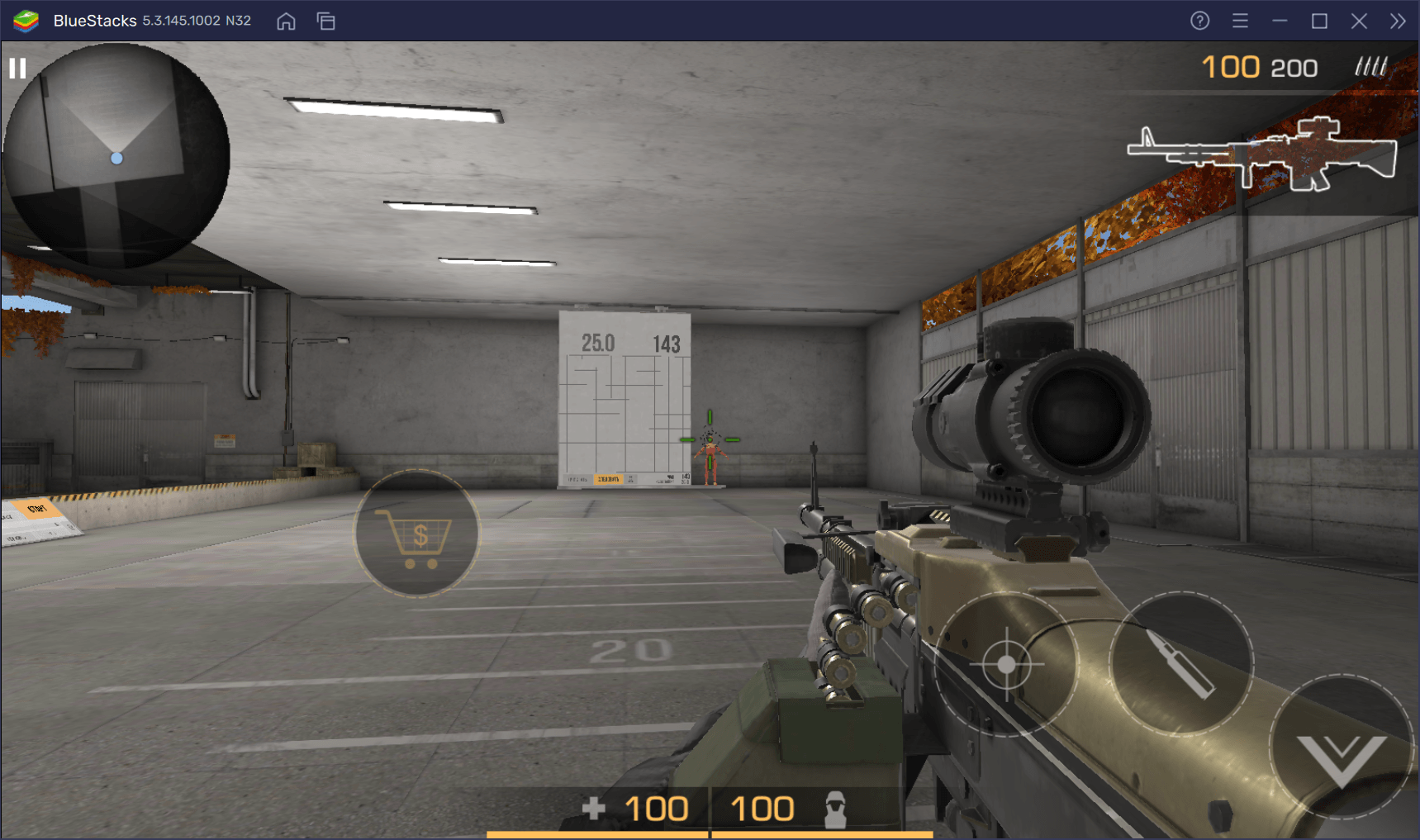
С 25 метров выстрел из M60 в незащищенную голову наносит 143 единицы урона, а в бронированную — около 130 единиц.
Еще одна особенность M60 заключается в задержке пули относительно нажатия на кнопку выстрела. Это стоит учитывать при подготовке к стрельбе и при паузе на стабилизацию. Если вы будете играть пулеметом против автомата, рекомендуем стоять очень плотно к укрытию, чтобы зайти за него после окончания стрельбы и не получить смертельный урон.
Как переносят оружие?
Пулемет М60 не оснащен ствольной ручкой. Обусловлено это тем, что ресурс ствола не превышает 200 выстрелов в режиме непрерывного огня. Было замечено, что после такой стрельбы ствол очень сильно нагревался, чем значительно усложнялась его замена. Чтобы обезопасить стрелка от ожогов, американскими конструкторами были разработаны быстросъемные стволы.

Кроме того, каждая модель комплектовалась асбестовыми рукавицами. Для переноски пулемета предназначалась специальная ручка, которая, по мнению американских солдат, не соответствовала весу пулемета. Место ее расположения также было выбрано не совсем удачно: носить пулемет при помощи данной ручки было неудобно, так как оружие при этом полностью теряло балансировку. Солдатами для переноски или удержания пулемета при стрельбе на ходу преимущественно использовались специальные ремни.
История создания[ | код]
В годы Второй мировой войны американская пехота так и не получила на вооружение удачной модели пулемёта; имевшиеся на вооружении пулемёты, в частности — Браунинга образцов , и годов и Джонсона образца 1941 года, представляли собой либо сильно устаревшие, либо просто неудачные образцы. Тем большим был интерес, с которым американская армия смотрела на новейшие немецкие разработки в этой области (впрочем, как и армии других стран, столкнувшихся с военной машиной Третьего Рейха).
«Винтовка парашютиста» FG-42.
Пулемёт MG 42.
В довоенные годы в Германии была создана концепция «единого» пулемёта, пригодного как на роль ручного, так и для стрельбы с самых различных станковых установок.
В годы войны в соответствии с ней был создан пулемёт MG 42, в своё время бывший своего рода эталоном для этого вида оружия.
Кроме того, на вооружение воздушно-десантных войск была принята «винтовка десантника» FG-42 (несмотря на сходство индексов с MG 42, это было совершенно иное по конструкции оружие), которая по сути представляла собой стреляющий с сошек лёгкий ручной пулемёт, который можно было использовать также в качестве самозарядной винтовки
Оба образца вызвали пристальное внимание американских военных.. Ещё до окончания боевых действий занимавшаяся до войны выпуском автомобильных запчастей для General Motors фирма Saginaw Steering Gear предприняла попытку конверсии MG 42 под американский стандартный винтовочно-пулемётный патрон 7,62×63 мм, но они окончились неудачей из-за значительной разницы в размерах боеприпасов (американский патрон был намного крупнее, чем немецкий 7,92-мм)
Ещё до окончания боевых действий занимавшаяся до войны выпуском автомобильных запчастей для General Motors фирма Saginaw Steering Gear предприняла попытку конверсии MG 42 под американский стандартный винтовочно-пулемётный патрон 7,62×63 мм, но они окончились неудачей из-за значительной разницы в размерах боеприпасов (американский патрон был намного крупнее, чем немецкий 7,92-мм).
После войны американцы, тщательно изучив немецкий опыт, приступили к созданию собственного «единого» пулемёта, при этом в качестве отправной точки были взяты именно упомянутые выше MG 42 и FG-42.
Первым опытным образцом был появившийся в 1946 году T44 под тот же 7,62×63 мм, от FG-42 он унаследовал всю работу автоматики, в частности — газовый двигатель с нижним расположением поршня и поворотный затвор, механизм же подачи ленты был скопирован с MG 42, с той лишь разницей что вместо горизонтального её движение стало вертикальным, снизу-вверх, а сам лентопротяжный механизм располагался на левой стороне затворной коробки — это было прямым наследием FG-42, у которой магазин располагался слева (по имеющейся информации, существовал также и ещё немецкий прототип FG-42 с аналогичным ленточным питанием).
В связи с грядущим принятием на вооружение нового «уменьшенного» патрона 7,62×51 мм НАТО (Т65) в 1948 году работы по Т44 были прекращены, хотя и дальнейшие разработки некоторое время всё ещё велись под старый боеприпас. Новый прототип, Т52, находился в разработке с 1947 по 1952 год. От вертикального движения ленты в нём уже отказались, приведя компоновку лентопротяжного механизма в полное соответствие с MG 42.
После 1952 года работы были продолжены над одним из его вариантов — T52E3, но под другим обозначением — T161. Указанные модели внешне ничем не отличались друг от друга, разница заключалась в технологии производства, — T52 и его модификации выпускались на заводе «Бридж» в Филадельфии, T161 на заводе «Инлэнд» в Дейтоне, — смена индекса преследовала целью выявить причину неудовлетворительных эксплуатационных отзывов, крылась ли она в исходно неудачной конструкции пулемёта или же была обусловлена различием набора технологических операций завода-изготовителя. Третья опытная модификация этого оружия, T161E1, была принята на вооружение под официальным обозначением machine gun, 7.62mm, M60 в 1957 году.
ЧИП — тюнинг
Но как же отличить М60Б30 от М60Б40? Последний мотор может использовать огромное количество спортивных валов с разными параметрами и стоимостью. Supercharger не нуждается в представлении и отлично выполняет все свои обязанности. Чтобы добавить двигателю нескольких десятков лошадиных сил, нужно купить валы для тюнинга. В этом случае могут быть полезными 272/258 с увеличенным подъемом. Такая приспособа M60B40 вместе с холодным впуском и выпуском в виде спортивной детали поможет добавить примерно 50 лошадиных сил к общей мощности. При установке более жестких валов и портировании ГБЦ можно получить еще пару десятков лошадиных сил. Но во втором случае авто превратится в некомфортное для города и окрестностей.
Другое неплохое решение, которое способно значительно улучшить показатели машины, может появиться вместе с покупкой компрессор кита. ESS после Vortech станет отличным решением, в комплекте с ним используется современный насос от известного производителя Bosch. Стандартная поршневая должна использоваться в данном случае по умолчанию, другие варианты только испортят характеристики. Такой набор сможет достичь давления в пол бара, а это поможет добиться результата в более чем 400 лошадиных сил. Этот вариант довольно интересен и его цена будет совсем немного выше, чем у предыдущего с атмосферными вкраплениями.
Модификации
Американскими оружейными конструкторами на базе единого пулемета М60 созданы несколько вариантов, использующих боеприпасы натовского образца калибра 7,62х51 мм:
- М60. Является базовым пулеметом. На вооружении американской пехоты и ВМФ числился с 1957 года.
- М60Е1. В отличие от базового пулемета, в котором местом крепления сошек стал ствол, в данной модели для установки сошек использовали газовую камеру.
- М60Е2. Данный вариант рассчитан для установки на военной технике. Приклады в этих пулеметах заменены рукоятками, а спусковые крючки – гашетками.
- М60Е3. Облегченная и усовершенствованная модель М60Е1. Пулемет оснащен пластиковым цевьем.
- М60Е4. представляет собой модифицированный пулемет М60Е3. При необходимости стрелок может устанавливать на данный вариант оптические или ночные прицелы.
- М60В. Пулемет разработан специально для стрельбы с вертолетов. Для конструкции оружия характерна пистолетная рукоятка. Эксплуатировались эти пулеметы с 1960 по 1970 год.
- М60С. Данный вариант пулемета также предназначен для стрельбы с вертолета. От предыдущей модели он отличается наличием электронного питания, позволяющего находящемуся в кабине пилоту производить стрельбу дистанционно.
- М60D. Данный вариант используется в армии США вместо М60В. Пулемет оснащен пистолетной рукояткой. В конструкции не предусмотрен спусковой крючок. Стрельба осуществляется при помощи гашетки. М60D эксплуатируется наземной, водной и воздушной боевой техникой.
General info
Survivability and armour
Smoke grenades
Creation of a smoke screen in front of the vehicle
Armourfront / side / back
Hull108 / 70 / 25
Turret230 / 49 / 57
Crew4 people
Visibility152 %
Armour type:
- Cast homogeneous armour — The main armour of the turret and hull.
- Rolled homogeneous armour — Engine deck and engine compartment rear, additional armour panels (upper and lower glacis).
- Structural steel — Slat armour, fenders, storage boxes.
- Gun steel — All gun barrels.
- Composite screens — Side skirts.
| Armour | Front (Slope angle) | Sides | Rear | Roof |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hull | 108 mm (65°) Upper Glacis 137 mm (52°) Lower Glacis 117 mm (55°) Lower Glacis (Bottom) 114 mm Turret Ring Guard | 36 — 70 mm Sides 50.8 mm Turret Ring Guard | 25 mm Engine Compartment Rear 40 mm Rear 28 mm Lower Rear 50.8 mm Turret Ring Guard | 36 mm Driver’s Compartment 20 mm Engine Deck |
| Turret | 230.9 mm Front Sides 76.2 mm Below and Above Mantlet 127 mm Gun Mantlet (Inner) 50.8 mm Gun Mantlet (Outer) | 53.8 — 230.9 mm Right Side 49.8 — 215.9 mm Left Side | 57 mm Turret Bustle Rear 25.4 mm Lower Rear and Bustle Underside | 48 mm Front 25.4 mm Rear |
| Cupola | 35 mm (Various Angles) Front 35 mm (Various Angles) Mantlet | 26 mm | 26 mm | 30 mm |
| Additional Armour | 6.35 mm Turret Front (Around Mantlet) 25 mm Upper and Lower Glacis | 65 mm Composite Screens Side skirts 10 mm Slat Armour Turret Sides 6.35 mm Front and Rear Track Guards | 10 mm Slat Armour Turret Rear | 25.4 mm Autocannon Platform |
Notes:
- The additional armour does not cover the entire face of the surface it is located on
- All Suspension Parts — 20 mm
- Tracks — 30 mm
- Turret Ring — 50.4 mm
- Fenders — 4 mm
- Storage boxes (4 mm) are mounted on top of the fenders
Mobility
Speedforward / back
AB65 / 16 km/h
RB and SB58 / 15 km/h
Number of gears6 forward
2 back
Weight54.5 t
Engine power
AB2 290 hp
RB and SB1 200 hp
Power-to-weight ratio
AB42.0 hp/t
RB and SB22.0 hp/t
| Game Mode | Max Speed (km/h) | Weight (tons) | Engine power (horsepower) | Power-to-weight ratio (hp/ton) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | Stock | Upgraded | Stock | Upgraded | ||
| Arcade | 65 | 16 | 54.5 | 1,860 | 2290 | 34.13 | 42.02 |
| Realistic | 58 | 15 | 1,061 | 1200 | 19.47 | 22.02 |
Modifications and economy
Repair costBasic → Reference
AB2 280 → 3 392
RB5 200 → 7 737
SB3 420 → 5 088
Total cost of modifications266 500
455 000
Talisman cost2 800
Crew training260 000
Experts930 000
Aces2 100
Research Aces1 080 000
Reward for battleAB / RB / SB
90 / 150 / 190 %
232 / 232 / 232 %
Modifications
| Mobility | Protection | Firepower | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Конструктивные особенности
Пулемет М60 конструктивно основан на автоматике с газовым приводом. Запирание ствола происходит под воздействием поворота затвора. Модель оснащена быстросменным стволом, что вызвано склонностью к его перегреву в ходе продолжительного огня. Питание патронами – ленточное. Что касается прицельного приспособления, последнее практически не отличается от образца, устанавливаемого на автоматическую винтовку М16.
Пулемет может устанавливаться на треноге либо на сошке. Максимальная дальность ведения огня составляет порядка 1800 м. На этом расстоянии сохраняется убойное действие оружия. Для гашения ударных нагрузок приклад комплектуется резиновой оболочкой.
History
The M60 is a second generation main battle tank, made by the USA. It is the fourth and last generation of the Patton family to replace the outdated M48 tank. It had officially entered service in 1962, the first user being none other than the US Army. The story of the Italian M60 begins during the late stages of the Cold War. During the early sixties, the Italian army’s tank arsenal did not appear up to standard, mainly due to having to entirely rely on America and other allies for military equipment, due to some laws surrounding the production of military arms. In fact, hundreds of tanks dating back to the Second World War were still being actively used in nearly all frontline units. Some of these units would include vehicles such as the M4 Sherman, M24 Chaffee, M36 Jackson, M10 Wolverine and the M26 Pershing. These tanks were now completely obsolete in the modern warfare setting; the leading vehicles of the Warsaw Pact, such as the T-54 and T-55, had already surpassed them in nearly every way. Thus the Italian Army Staff (SME) therefore deemed it necessary to improve the operational capability of the national tank component by following two lines of action. The first one was to continue the introduction of M47s from other NATO armies, that had usually been obtained at very favourable prices, even despite having to entirely rely on foreign countries. The other line of action was to keep on introducing newer vehicles at a modest rate, with modern performance and ability to compete with the best and latest main battle tanks coming out of the Warsaw Pact. In general, there was a need for a more powerful MBT, that even the M47, one of the most powerful tanks they had at the time, couldn’t be on par with. The M47, in fact, although being appreciated by its users for its sturdiness, ease of use, decent mobility and enough firepower to deal with most modern tanks at the time, it sadly did not fully satisfy the requirements of the «Ariete» and «Centauro» divisions. This meant that something had to be done, and had to be done fast.
During that period of time, Italy did not actually end up having much choice to pick from. Choices would be restricted to the US M60, the British 37t Chieftain and Vickers, and the so-called «standard» tanks at the time would still be under heavy development in France and West Germany, which would come out with AMX-30 and the Leopard 1 MBTs. The British solution was absolutely not favoured, Italian high command deeming the tanks being too slow and heavy for the Italian operational environment, and generally didn’t go hand in hand with the Italian doctrine at the time. In addition, they also evaluated the lifespan and potential upgrades that could be done at a later date to keep the tanks in service for as long as possibile, and the only one to really yield positive results would end up being the American M60.
After a long evaluation test period, and training with the machine to familiarize the future users of the vehicle, the Italian army would possess 200 M60A1s by the 1970s, license-produced by OTO Melara in Italy, and an additional 100 from excess USA-EUR stocks. The M60 in Italian service was used by several armoured divisions, including the Armored Division Ariete, 32nd Armored Brigate Mameli, 60th Armored Battalion Pinerolo, 20th Tank Battlalion Pentimalli, 8th Tank Battalion Secchiaroli, and 10th Tank Battalion Bruno. They would widely be used in a lot of theatres of war in which Italy was involved, such as Lebanon in Operation LIBANO 1 and LIBANO 2, and more famously they also partook in the Somalia intervention where M60 tanks would be used in the frontlines of the conflict. Eventually, even the M60 had to be gradually phased out with the end of the Cold War, not only because multiple countries had started to work on more advanced vehicles, but also because a lot of militaries at the time had started to quickly downsize their stockpile of tanks as the threat of a Soviet invasion no longer loomed. It would be completely replaced by C1 Arietes by the 2000s, however a few years ago, Leonardo, an Italian defense company, had presented an upgrade to the M60 tank known as the Leonardo M60A3 upgrade, which heavily modernized the M60 tank, to make it suitable for the modern setting. This was primarily done to allow countries who still used the M60 tank to receive an upgrade which would extend the life of the M60 even longer, by upgrading key aspects of the tank that made it unsuitable for the current setting. Such changes included a new engine, a new 120 mm cannon, thermal imaging devices and improved armour.
The M60A3 (1980)
Work on a vastly enhanced version began in 1978, at the same time the M1 Abrams program began. This was chiefly to keep the M60 in operation alongside the much costlier new main battle tank, and to be able to face off the T-64 and T-72. Although the hull and turret remained unchanged for the most, it was easily distinguished by the fitting of two banks of smoke dischargers, an AN/VVG-2 flash-lamp pumped ruby-laser based rangefinder, an M21 ballistic computer and a turret stabilization system. At mid-production, it was also decided to delete the cupola.
This was done for three reasons. Israeli studies on their own M60A1/A3s in combat (IDF tactical doctrine imposed that the commander fight unbuttoned, exposed) showed that a non-penetrating hit on the turret roof, burying itself at the base of the cupola (acting as a shot trap) could dislodge it, instantly killing the commander. In addition, the locking mechanism of the hatch was dangerous to use under fire. The performances of the remote-controlled M85 heavy AA MG as originally intended were even worse than those of the pintle-mount cal.50 (12.7 mm), due to limited elevation. Therefore, late versions are recognized by their low-profile, simpler “Urdan cupola”, and the overall silhouette of the tank was greatly diminished in the process.
M60A3
The service duration of the M60A3 was impressive, spanning two and a half more decades, from 1980 to 2005. This was due to a number of factors, that made it compare well with the much more advanced M1, especially from a cost and maintenance point of view. The infantry telephone on the back plate was still on the M60 but was eliminated on the M1 and later retrofitted with TUSK. Although having lower performance, the M60 engine was much cheaper to maintain, more fuel-efficient and had also a lower temperature. It was, therefore, less dangerous for infantry marching behind.
The floor escape hatch, absent on the M1, was also an added safety feature for the crew, if the tank was turned over or under enemy fire. Indirect fire was also easier on the M60 and allowed a more variety of operations in coordination with infantry. So, in tactical doctrine, the M1/M60 rôles were refined and well distributed. The M1 Abrams was to spearhead the armored assault and deal with enemy tanks, while the M60 was to follow with infantry to clear and sanitize the area, especially in an urban environment. However, both tanks were equally sensitive to IEDs.
105mm Gun Tank M60 links & resources
The 105mm Gun Tank M60 on WikipediaOn Military-factory
105mm Gun Tank M60 equipped with a mine plough on training at the Quantico USMC base.
External links
- M60
- U.S. medium tank M60
| Chrysler Defense | |
|---|---|
| MBTs | M48 Patton · M60 · M60A1 (AOS) · M60A2 · M60A1 RISE (P) · M60A3 TTS · XM-1 (Chrysler) · M1 Abrams |
| Note | Chrysler Defense was purchased by General Dynamics Land Systems (GDLS) in 1982. |
| USA medium tanks | |
|---|---|
| M2 | M2 |
| M3 | M3 Lee · ▃Grant I |
| M4 | M4 · Calliope · M4A1 · M4A1 (76) W · M4A2 · M4A2 (76) W · M4A3 (105) · M4A3 (76) W |
| M26 Pershing | T20 · T25 · M26 · M26 T99 · M26E1 |
| M46/47/48 Patton | M46 · M46 «Tiger» · M47 · M48A1 · T54E1 |
| M60 | M60 · M60A1 (AOS) · M60A1 RISE (P) · M60A2 · M60A3 TTS |
| MBT-70 | MBT-70 · XM-803 |
| M1 Abrams | XM-1 (Chrysler) · XM-1 (GM) · M1 Abrams · IPM1 · M1A1 Abrams · M1A1 HC · M1A2 Abrams |
| Other | T95E1 |
| Canada | M4A5 |
| Israel | Magach 3 · Merkava Mk.1 · Merkava Mk.2B · Merkava Mk.3D |
| Turkey | M60 AMBT |
Usage in battles
The M60 AMBT excels as a tank which is able to defend cap zones and destroy foes at far ranges. However, it lacks the protection of other MBTs. The main weaknesses of the M60 AMBT are the armour and pure size of it. All enemy tanks which it engages within combat are able to penetrate it with ease.
The cannon is the same cannon which you find in the M1A2, It offers great penetration, able to penetrate the toughest of foes. Its armour is that of an M60s. It also shares the same platform as the M60s. It’s a tall, high profile tank, which can be seen with ease. However, an advantage of this is it’s able to see over objects which most MBTs can’t see over, due to their sleek low profile designs.
The M60 AMBT offers thermal sights, which allow it to spot the heat source of the enemy tanks, additionally it has a 25 mm LW25 grenade launcher which can cause major damage to critical parts of the enemy. Using its 25 mm HE grenades to knock out the enemy tank cannons and de-track them preventing them from escaping to safety. To get the best out of this tank, at long range, use the 120 mm cannon to snipe them to do this setup an ambush, watching their cap zones, engage thermal sights and await for the them to come. At close and medium ranges use the map and sneak up on the enemy foes, using the thermal sights to gain your advantage.
Handling air threats
To defeat these threats, scan the skies with the thermal sight and you will see the heat source of them. If they are approaching you or have fired a missile — pop smoke and withdraw, await for your SPAA to shoot them down, make sure to tag them on the map!
If the helicopter is close, shoot it with your main 120 mm cannon a single hit will see the tail drop of it. Now if the helicopter is right on top of you or within in machine gun range, use the 25 mm grenade launcher which will be able to bring it down with a few well placed bursts. Aim, for the flight deck and engine compartment. The M3P heavy machine gun also has a very fast fire rate which can deter enemy aircraft.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- High penetrating APFSDS round, allowing effective engagement of any target from the front.
- Has much higher mobility than the other M60 series tanks, making it much more pleasant to play.
- Has a 25 mm autocannon on the turret roof, allowing easier engagement of low-flying helicopters.
- Is protected on the sides by composite screens and slat armour which can protect against HEAT projectiles and low-penetration autocannons, though it should not be relied upon.
- No ammunition is located in the turret bustle, which means shots to the turret will almost never kill it in one shot.
- Has good gunner and commander Thermal optics (800×600)
Cons:
- Has a stock HEATFS round with the APFSDS round as a Tier III modification; HEATFS can be useful but is generally less effective and versatile than APFSDS.
- Lacks useful armour such as composite or spaced armour: just about any shell that hits it is going to penetrate except for low-penetration autocannons from the front.
- Has a very large and weak mantlet which is able to be penetrated by high-penetration autocannons, such as those on the CV90 series; the turret ring is a target for even weak autocannons.
- Despite the much more powerful engine when compared to earlier M60s, the AMBT still does not have the mobility of the other MBTs at its BR.
- The commander’s cupola is very large and the 25 mm gun is mounted high above the turret, and they will often give away your position, especially when trying to go hull down or when cresting a hill or ridge.
- Relatively tall silhouette, enemies have no problem identifying and spotting you.
Эксплуатанты[править]

Корейские солдаты с M60 проводят высадку морского десанта в ходе учений Foal Eagle 07.
 Боевик Исламского освободительного фронта моро лежит с M60.
Боевик Исламского освободительного фронта моро лежит с M60.
V-150 Commando португальской армии с M60D.
Военнослужащий с М60 на авиабазе Шпангдалем, Германия.
- Австралия Австралия: постепенно заменяется на FN Minimi и FN MAG.
- Алжир Алжир
- Боливия Боливия
- Босния и Герцеговина Босния и Герцеговина
- Великобритания Великобритания: используется в Королевских ВВС; монтируется на Чинуки.
- Венесуэла Венесуэла
- Гаити Гаити
- Гана Гана
- Гондурас Гондурас
- Греция Греция
- Дания Дания: начиная с 2015 года, датской армией будет получено более 600 M60E6 в качестве замены M/62.
- Демократическая Республика Конго Демократическая Республика Конго
- Доминиканская Республика Доминиканская Республика
- Индонезия Индонезия
- Иордания Иордания
- Италия Италия
- Камбоджа Камбоджа
- Колумбия Колумбия
- Коста-Рика Коста-Рика
- Либерия Либерия
- Ливан Ливан
- Литва Литва: Получено 75 M60 в 2002 году от американского агентства Defense Logistics Agency из МО США.
- Люксембург Люксембург: На службе в 1957—1972 гг.; заменяется на FN MAG.
- Малайзия Малайзия: M60E3 используется армейским спецназом.
- Марокко Марокко
- Никарагуа Никарагуа
- Панама Панама
- Перу Перу
- Польша Польша: ограниченное количество М60 было приобретено вместе с фрегатами типа «Оливер Хазард Перри».[источник не указан 2328 дней]
- Португалия Португалия: португальская армия использует M60E и M60D для монтажа на V-150 Commando.
- Республика Корея Республика Корея: Лицензионное производство 1974—2011. Заменён на К12.
- Сальвадор Сальвадор
- Сенегал Сенегал: получены в подарок 2500 M60 в 2002 году от Defense Logistics Agency МО США.
- Сент-Винсент и Гренадины Сент-Винсент и Гренадины
- Судан Судан
- США США: используется Армией США и SEAL.
- Китайская Республика Китайская Республика: производился под индексом Тип 57.
- Таиланд Таиланд
- Тринидад и Тобаго Тринидад и Тобаго
- Тунис Тунис
- Турция Турция
- Уганда Уганда
- Фиджи Фиджи
- Филиппины Филиппины
- Чехия Чехия: M60E4 используются частью спецподразделений Чешской армии. Известно приобретение М60 601-м отрядом спецназа в 2006 для замены пулемётов UK vz. 59L.
- Чили Чили
The 105mm Gun Tank M60 in action
Due to an impressive service length span, the M60 and variants participated in some major conflicts and many operations. The most important such battle theatre also saw the most number of M60 of many nations engaged, within the coalition forces in 1991 (Operation Desert Storm).
In US service, the M60 never saw service in Viet-nâm, contrary to the M48. For the US Army, the only operations were at Grenada (1982), Beirut (1983), and the Gulf War (1991). In the mid-1980s, close air support trials took place along with ground-combat equipped F-16s and pioneered tactical doctrines and technologies later used with M1 Abrams-equipped units. These occurred notably at the Red Flag exercise at Nellis AFB Nevada. After the end of the Cold War, most of the M60s (which were USMC M60A3s) were placed in reserve and only specialized variants were kept in service, like the M728 Combat Engineer vehicle and the bridgelayer version AVLB.
Yom Kippur War (1973)
The M60 was first blooded during this war opposing Israel to Egypt, Syria and Jordan. About 150 M60A1 (E60A) were opposed, with success, to the Egyptian-operated T-54/55 and T-62. But, at the same time, in the Bar-Lev line, they were destroyed in rows by Egyptian-manned portable AT-3 Sagger shaped-charge missiles, following the Egyptian crossing of the Suez Canal. Due to their effective gun, mobility and excellent safety records, IDF M60s had been highly regarded and were upgraded significantly, leading to the Magach 6/7 types and the Sabra for the export market. During this conflict, Jordan also possessed M60A1, but none was deployed.
Iran–Iraq War (1982-89)
The Iranian M60s were seriously tested against Iraqi T-55, T-62 and T-72s, and performed well alongside some M48s. Before the revolution, Iran had some 350 M60A1s, but this number dwindled rapidly due to the lack of maintenance and spare parts, to the actual figure of 150 tanks in 2011. At least one M60 was captured by Iraqi troops, evaluated, and was found in Baghdad in 2003.
Lebanon War (1982)
The Israeli Magach 6 formed the core of the armored forces involved in Operation Peace in Galilee, dealing with Syrian T-54/55 and T-72s or even ex-PLO T-34/85s. The only loses occurred when encountering Syrian infantry hunter-killer teams using ATGMs, RPG-7s and SA-7 Grail MANPADs. HOT missiles fired from Syrian Gazelle helicopters were also deadly. A single M60 was damaged, evacuated by its crew and shipped back to Syria to be studied by Soviet technicians, which gave them clues about the latest NATO ammunition on board. It is now still on display in Damascus.
First Gulf war (1991)
During Operation Desert Storm in February 1991, USMC’s M60A1 ERA rolled into Kuwait City after a fierce battle at the Kuwait Airport. Some 200 participated in the largest tank battle for an USMC unit since World War Two, dealing with Iraqi T-54/55, Type 69, and T-72 tanks, north from Khafji. This unit claimed nine dozen Iraqi tanks destroyed for a single M60A3 lost.
At the same time, USAF 401st TFW (P) unit used M60s based in Doha AFB, Qatar, modified to deal with unexploded ordnance from tarmac runway and taxiway surfaces. Saudi, Egyptian and Omani forces also deployed their own M60s in this operation.
Operations in Afghanistan (2002-2012)
Only specialized variants were deployed, having a great deal of activity altogether in several sub-operations at tactical organic unit level, notably to create provisional bases and depots.








