Oh-58 kiowa
Содержание:
- Essential Specifications
- OH-58F Block II
- Armament
- Hellfire missiles
- successeur
- Sergilenen uçak
- Polychop объявляют о выпуске OH-58D Kiowa для DCS World
- Вы здесь
- Honeywell HTS900 engine (OH-58F)
- OH-58D cockpit
- Kiowa weapons
- Rolls-Royce M250-C30R/3
- Operators:
- Исторический
- Armement
- Технические характеристики Bell OH-58 Kiowa.
- Hydra-70 Family
- 2.75-inch/70mm DAGR missile
- Countermeasures
- succesor
- Utilisateurs
Essential Specifications
| Cruise Speed with Weapons | 95 kts | 176 kph |
| Range | 140 nm | 260 km |
| Seating | 2 crew seats in cockpit | |
| Maximum Gross Weight | 5,500 lbs | 2,495 kg |
| Powerplant | One (1) Rolls-Royce 250-C30R3 | |
| 650 shp | 485 kW |
Source scoutsout.com
OH-58F Block II

OH-58 Block II demonstrator
Bell says the OH-58 Block II demonstrator “takes an OH-58 Kiowa Warrior and makes it a fast-fielding, low-risk and lowest-cost solution” to the Army’s expected “high-hot” operational requirement of 6,000-foot, 95-degree performance. That performance can be attained with propulsion and drive-train upgrades to the existing platform, the company says.
The Block II aircraft builds on the OH-58F-model cockpit and sensor upgrade program (CASUP) by adding a new Honeywell HTS900 engine, transmission and rotor system. The CASUP program replaces the OH-58D’s mast-mounted sensor with a nose-mounted sensor, updates the cockpit with color, multifunction displays, and incorporates full authority digital engine control and common missile warning system. As with the EADS candidate helicopter, the OH-58 Block II aircraft can be fitted with M3P machine gun, 2.75-inch rockets and Hellfire missiles. Source ainonline.com
Armament
OH-58D «Kiowa Warrior»
Configurația armei este de obicei aleasă astfel încât o echipă de două elicoptere să poarte un amestec de arme posibile. Se spune că prima escadronă a 17-a cavalerie a armatei SUA are în jur de 15 războinici Kiowa într-o versiune puțin observabilă . În acest scop, mașinile au fost acoperite cu materiale absorbante radar pentru a reduce secțiunea transversală a radarului .
- Sarcină utilă de până la 907 kg pe două cadre de încărcare externe
- Rachetă ghidată aer-aer
2 × lansatoare de rachete duble ATAS (Air To Air Stinger) pentru 2 × Raytheon AIM-92 «Stinger» RMP Block I fiecare — controlat în infraroșu pentru distanțe scurte
- Rachete aer-suprafață neguidate
- 2 × LAU-260 / Containere de lansare a tubului de rachetă pentru 7 × rachete aer-suprafață Hydra neguidate fiecare ; Calibru 68 mm / 2,75 inch
- 2 × LAU-68D / A containere de lansare a tubului de rachetă pentru 7 × rachete hidraulice FFAR aer-sol neguidate fiecare; Calibru 70 mm
- 2 × LAU-131 / A containere de lansare a tubului de rachetă pentru 7 × rachete hidraulice FFAR aer-sol neguidate fiecare; Calibru 70 mm
- Rachete ghidate aer-suprafață ( rachete ghidate antitanc )
2 × suspensii de rachete ghidate M299 pentru 2 × Boeing Corp / Martin Marietta AGM-114F / N «Hellfire» — controlate cu laser
- Butoi de tun extern
- 2 × sisteme de arme M-27 constând fiecare din 1 × 7,62 mm mitralieră Gatling General Electric M134 cu 2000 de runde de muniție fiecare
- 2 × 12,7 mm mitraliere Browning M296 cu 500 de runde de muniție fiecare
- 2 × trei mitraliere 12,7 mm mitralieră Gatling General Dynamics GECAL 50 ( GAU-19 / A) cu 2000 de runde de muniție fiecare (cadență: 2000 sau 4000 de runde / min; autonomie de până la 1000 m)
Hellfire missiles

Aircraft throughout the years
Primary Function: Air-to-surface and surface-to-surface point target/anti-armor missilePrime Contractor: Hellfire Systems, LLC – A Boeing – Lockheed Martin Joint VenturePropulsion: ATK (now Orbital ATK) solid propellant rocket motor (IM HELLFIRE Propulsion System);
AGM-114A: ATK M120E3; AGM-114B: ATK M120E4; AGM-114L: ATK M120E4Length: 5.33 ft (1.62 m); AGM-114L: 5.77 ft (1.76 m)Diameter: 7 in (17.8 cm)Wingspan: 28 in (0.71 m)Weight: 98 to 109 lbs (44.5 to 49.4 kg); AGM-114R: 109 lbs (49.4 kg)Speed: SubsonicRange: AGM-114 K/L/M/N: 4.97 miles (8,000 m)
AGM-114R fired at 3,000 ft (914 m):
4.97 miles (8,000 m) – LOAL, high trajectory
4.41 miles (7,100 m) – LOAL, low/direct trajectoryGuidance: Semi-Active Laser (SAL) seeker; AGM-114L: Millimeter wave (MMW) radar seekerWarhead: AGM-114 A/C/F/K/K-2/L/P/P+: Shaped charge warhead
AGM-114F-A/K-2A/P-2A: Shaped charge warhead with frag sleeve
AGM-114M/N: Blast fragmentation warhead (AGM-114N is a thermobaric version with metal augmentation charge)
AGM-114R: Multi-purpose Integrated Blast Frag Sleeve (IBFS) warhead
Source fi-aeroweb.com
successeur
Puisqu’il y a eu de lourdes pertes en Irak et que les hélicoptères, dont certains ont presque 40 ans, atteignent lentement la fin de leur durée de vie, l’ hélicoptère de reconnaissance armé (ARH) a été mis en appel d’ offres le 9 décembre 2004 . Bell Helicopter Textron a participé avec le Bell 407 , MD Helicopters, cependant, avec un MH-6 Little Bird modernisé . Le 29 juillet 2005, l’armée américaine a annoncé le Bell 407 comme le gagnant de l’appel d’offres ARH. L’hélicoptère basé sur le Bell 407 s’appelait désormais ARH-70A et devait remplacer les anciennes machines Kiowa à partir de 2008, l’achat de 368 hélicoptères étant prévu. Le 16 octobre 2008, cependant, le Pentagone a annoncé qu’il arrêterait l’acquisition de l’ARH-70. La raison en était la performance insuffisante et le dépassement des coûts d’acquisition.
EADS propose à l’armée américaine un successeur, l’ Armed Scout 645 , actuellement en phase de développement et de démonstration. En attendant, il y a des tentatives pour équiper les hélicoptères existants de nouveaux instruments de cockpit en verre ; la phase d’offre est prévue pour 2011.
En mai 2014, l’armée américaine a commencé à réduire la flotte de Kiowa . Les hélicoptères déclassés doivent être proposés à la vente à d’autres forces armées.
Sergilenen uçak
- 68-16940 — Uluslararası Havaalanı içinde Palm Springs, California . Heykele dönüştürülmüş.
- 69-16112 — Pima Hava ve Uzay Müzesi de Tucson, Arizona
- 69-16123 — Askeri Tarih Kansas Müzesi içinde Augusta, Kansas
- 69-16153 — MAPS Hava Müzesi içinde North Canton, Ohio
- 69-16338 — Nokta Alfa Müzesi içinde Hesse, Almanya
- 71-20475 – Veterans Memorial Museum , Huntsville, Alabama , Amerika Birleşik Devletleri
- 71-20869 – Kanada Ulusal Hava Kuvvetleri Müzesi , Trenton, Ontario , Kanada CH-136
- 71-20920 – Polonya Havacılık Müzesi , Krakov , Polonya – CH-136
- 72-21256 — Kentucky , Lexington’daki Kentucky Havacılık Müzesi
Polychop объявляют о выпуске OH-58D Kiowa для DCS World
13 дек
2019
Вот небольшой отрывок из анонса Polychop Simulations, полный текст которого вы можете прочитать на нашем форуме.
Дорогие друзья,
Уже прошло несколько месяцев с тех пор, как мы впервые публично объявили о том, что работаем над OH-58D Kiowa для DCS World.
В течение последних двух лет мы плотно занимались Bell OH-58D Kiowa Warrior. Мы не знали заранее, для какого игрового симулятора мы создадим OH-58D, но в какой-то момент мы решили, и уже во второй раз, обратиться к DCS.
За эти 2 года мы наработали очень много рабочих контактов со специалистами из Bell Textron, Eagle Dynamics, с представителями разведывательных вертолетных частей сухопутных войск США.
Bell Textron выдала нам лицензию на использование вертолета OH-58D Kiowa Warrior в коммерческих целях, что означает, что нам было дано разрешение на создание модели вертолета для развлекательных задач. Без этой лицензии модуль для среды DCS World был бы невозможен.
С лицензией также приходит ответственность. Все, что связано с продуктом, будет подвержено строгим процедурам контроля качества. Мы осознаем это как возможность и преимущество для общества при моделировании OH-58D Kiowa Warrior в DCS World, так и для себя, как развивающейся компании. Лицензия также предоставила нам доступ к определенной информации, которая была недоступна публично. Без этой информации было бы невозможно воссоздать реалистичное поведение вертолета.
После получения лицензии производителя мы связались с компанией Eagle Dynamics, чтобы обсудить с ней наши планы. Это был длительный процесс, в течение которого велись переговоры о заключении возможных контрактов. Переговоры подобного рода сложны, особенно если присутствует третья заинтересованная сторона, в данном случае, Bell Textron. В конце концов, все стороны достигли окончательного соглашения.
В октябре 2020 года, буквально за день до начала выставки авиасимуляторов в Косфорде, мы получили зеленый свет от Eagle Dynamics на работы по интеграции модуля OH-58D Kiowa Warrior в DCS World. Несмотря на то, что окончательный контракт еще не был заключен на тот момент, мы понимали, что серьезных препятствий для работы уже не существует, и в той или иной удовлетворяющей всех форме он будет подписан.
На текущий момент мы можем говорить, что договоренности достигнуты, а контракт подписан. Модуль OH-58D Kiowa Warrior будет выпущен в виде DCS World модуля. Мы пока не можем назвать дату выхода. Однако определенно мы это планируем сделать в 2020 году.
Мы очень рады тому, что у нас у всех появилась возможность реализовать этот вертолет в DCS World. Эта интересная и легендарная машина теперь будет в виртуальном небе DCS. Мы хотим поблагодарить Eagle Dynamics, в особенности Ника Грея (Nick Grey) и Мэттиаса Техмански (Matthias Techmanski) за поддержку и доверие, оказанное нашей команде в том, что мы сможем достойно воссоздать эту винтокрылую машину с первым в США “стеклянным кокпитом”.
Нам осталось определиться как и когда сообщество будет получать информацию о развитии модуля, новые видео и стримы. На настоящий момент мы договариваемся о проведении онлайн стрима с некоторыми из очень интересных людей. Что будет обсуждаться, с кем и когда вы сможете узнать через несколько дней. Оставайтесь с нами. Спасибо всем, Polychop Team
Вы здесь
Главная » Блог » Прочие » Вертолёт Bell OH-58 Kiowa. Технические характеристики. Фото. 2016-04-26

Прочие
Вертолёт Bell OH-58 Kiowa. Технические характеристики. Фото.
Bell OH-58 Kiowa – американский военный многоцелевой вертолёт, разработанный авиастроительной корпорацией «Bell Helicopter» в 1966 году.
Фото Bell OH-58 Kiowa
Проект американского многоцелевого военного вертолёта стал разрабатываться специалистами по специальному заказу Вооружённых сил США. Связано этом было с необходимостью поступления в вооружённые силы страны качественных многоцелевых летательных аппаратов, способных обеспечивать огневое прикрытие и использоваться в качестве полноценных боевых единиц, способных вести борьбу с отрядами противника, включая живую силу, легкобронированную и бронированную технику. Разработка исключительно ударного вертолёта не интересовала представителей военного командования США, поскольку, в подобной ситуации, летательный аппарат не мог использоваться для переброски небольших групп людей и их эвакуации.
Первые работы по созданию многоцелевого военного воздушного средства начались американскими авиастроителями ещё в 1961 году, и фактически, полный процесс разработки вертолёта занял 5 лет, что привело к некоторому удорожанию воздушного судна, однако, из-за того, что летательный аппарат разрабатывался исключительно для военных нужд, это практически не отразилось на его популярности.
Bell OH-58 Kiowa фото
В 1966 году вертолёт Bell OH-58 Kiowa произвёл своё первый тестовый полёт, который оказался весьма впечатляющим, однако, ряд конструктивных особенностей воздушного судна требовал дополнительных доработок, в связи с чем, производство данного летательного аппарата началось лишь в 1969 году.
На своём борту вертолёт модели Bell OH-58 Kiowa может осуществлять транспортировку шести человек, включая двух пилотов, либо же одного пилота и стрелка, а также четырёх военнослужащих, либо равный по массе объём дополнительного груза. Благодаря тому, что воздушное судно обладало многоцелевым назначением, вертолёт получил большую поддержку, в связи с чем выпуск его вёлся вплоть до 1989 года.
Вооружение вертолёта Bell OH-58 Kiowa включает в себя один пулемёт с блоком из 6 вращающихся стволов, и может дополнительно экипироваться двумя комплектами неуправляемых ракет для поражения бронированной техники противника, либо же для обеспечения огневого прикрытия с воздуха. При необходимости, здесь же могут устанавливаться и два ручных крупнокалиберных пулемёта, однако, в этом случае, экипаж воздушного судна должен быть увеличен до четырёх человек.
Вертолёт Bell OH-58 Kiowa
Силовая установка вертолёта модели Bell OH-58 Kiowa состоит из одного газотурбинного авиационного двигателя марки Allison T63-A-700, который способен развивать тягу в 317 л.с., что весьма немного для военного вертолёта. Тем не менее, авиадвигатель обладает высокой надёжность и обеспечивает летательному аппарату возможность разгоняться до скорости в 220 км\ч. (в зависимости от модификации вертолёта). Вертолёт может осуществлять авиаперелёты на дистанциях до 480 километров, что является весьма приемлемым для данного типа воздушного судна.
Производство вертолётов модели Bell OH-58 Kiowa осуществлялось американскими авиастроителями в следующих вариантах:
- Bell OH-58A Kiowa – базовый четырёхместный производственный вариант воздушного судна;
- Bell OH-58B Kiowa – экспортный вариант вертолёта, разработанный по заказу ВВС Австрии;
- Bell OH-58C Kiowa – модернизированная версия с более производительной силовой установкой и рядом технических улучшений;
- Bell OH-58D Kiowa – улучшенный вариант вертолёта, с более мощным вооружением и рядом технических дополнений и улучшений;
- Bell OH-58F Kiowa – модернизированный вариант вертолёта, представленный в 2012 году;
- Bell OH-58F Block II – одна из разновидностей вертолёта версии Bell OH-58F Kiowa;
- Bell OH-58X Kiowa – специальный экспериментальный вариант вертолёта.
Honeywell HTS900 engine (OH-58F)
 “The Honeywell HTS900 engine is a new type design engine to provide superior performance at high, hot conditions, fuel efficiency, and operating costs” said Mike Cuff, Honeywell Vice President, Helicopters and Surface Systems. “This certification demonstrates Honeywell’s continued success in developing the world’s highest performance turboshaft engines for both the commercial and military segments.
“The Honeywell HTS900 engine is a new type design engine to provide superior performance at high, hot conditions, fuel efficiency, and operating costs” said Mike Cuff, Honeywell Vice President, Helicopters and Surface Systems. “This certification demonstrates Honeywell’s continued success in developing the world’s highest performance turboshaft engines for both the commercial and military segments.
“The Honeywell HTS900 engine produces more than 1,000 Shaft Horsepower (SHP) uninstalled at sea level on a standard day – and has accumulated more than 1,000 flight hours,” Source aero-news.net
OH-58D cockpit

The Kiowa was the first US Army helicopter to have an all-glass cockpit. The cockpit is supplied by Sperry Flight Systems and is equipped with a multiple target tracking / moving target indicator, an ANVIS (aviation night-vision system) display symbology system and helmet-mounted display.
The primary multifunction displays provide situation information, communications control and the mast-mounted sight video. A video recorder stores television and thermal imagery from the mission and allows playback in the cockpit.
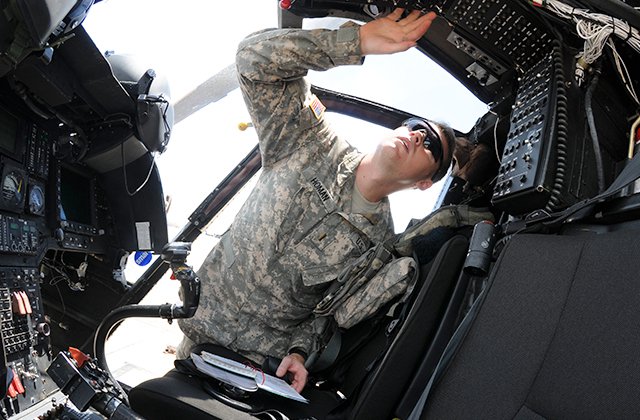

Kiowa weapons
The OH-58D is equipped with two universal quick-change weapons pylons. Each pylon can be armed with two Hellfire missiles, seven Hydra 70 rockets, two air-to-air Stinger missiles or one .50-calibre fixed forward machine gun.
Rolls-Royce M250-C30R/3
One Allison 250-C30R (T703-Ad-700) turboshaft, (C30R/3 with improved diffuser in Kiowa Warrior) with an intermediate power rating of 485kW at S/L, ISA, FADEC. Transmission rating: Kiowa 339kW continuous; Kiowa Warrior 410kW continuous. One self-sealing crash-resistant fuel cell, capacity 424 litres located aft of the cabin area. Refuelling point on starboard side of fuselage. Oil capacity 5.7 litres. Source aviastar.org

Image: Rolls-Royce

fi-powerweb.com
Operators:
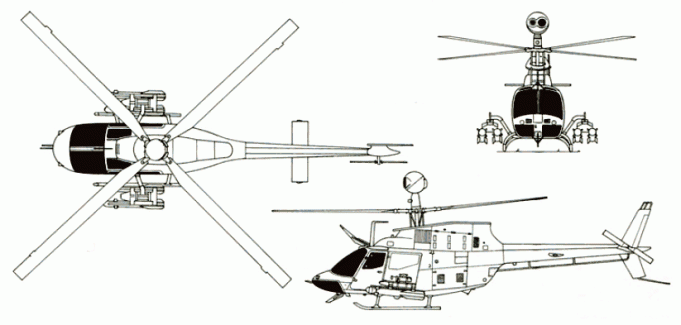
| Entered service | 1985 |
| Crew | 2 men |
| Dimensions and weight | |
| Length | 12.9 m |
| Main rotor diameter | 10.67 m |
| Height | 3.95 m |
| Weight (empty) | 1.74 t |
| Weight (maximum take off) | 2.5 t (?) |
| Engines and performance | |
| Engines | 1 x Allison turbine |
| Engine power | 650 shp |
| Maximum speed | 240 km/h |
| Cruising speed | 205 km/h |
| Service ceiling | 4.58 km |
| Range | 555 km |
| Armament | |
| Cannon | pod with 12.7-mm machine gun or 40-mm automatic grenade launcher |
| Missiles | up to 4 x AGM-114 Hellfire anti-tank missiles or up to 4 x FIM-92 Stinger anti-aircraft missiles |
| Rockets | 2 x Hydra 70 rocket pods with unguided rockets in place of the missiles |
Technical data military-today.com
Main material source army-technology.com
Images are from public domain unless otherwise stated
Main image Joint Combat Camera Center Iraq / Photo by Petty Officer 1st Class Carmichael Yepez
Revised May 04, 2017
Updated Nov 14, 2021
Исторический
OH-58A поступил на вооружение армии США в мае 1969 года, они были развернуты в Южном Вьетнаме с 17 августа 1969 года, где они завершили и заменили в своей миссии разведки и артиллерийского наблюдения Hughes OH-6 Cayuse во время войны во Вьетнаме . Когда они работают в сочетании с ударными вертолетами AH-1, они образуют Розовую команду , розовую команду. OH-58 — это Белая птица, а AH-1 — Красная птица .
375 OH-58D, поставленные в армию США с 1985 года, заменили AH-1 Cobra и OH-58A и C, включая разведывательные миссии. 115 Kiowas были задействованы во время операции «Буря в пустыне» в 1991 году, налетав у них 9000 часов.
В ходе операции «Свобода Ираку» в 2003 г. было задействовано 120 вертолетов Kiowa . 35 вертолетов были потеряны в войне в Афганистане с 2001 г. и в войне в Ираке с 2003 г. Флот Kiowa достиг 820 000 часов налетов в боевых действиях в конце 2013 г. В 2013 г. — 330 вертолетов. находятся на вооружении армии США, в том числе 30 в Национальной гвардии.
В феврале 2014 года, предлагается , чтобы она была удалена 2017. 1 — й эскадрильи, 17 — го кавалерийского полка (в) ( 3 — й стрелковой дивизии ) из базы Hunter в Savannah , который является последним в 2016 году , чтобы сохранить 22 из этих самолетов обменять их на AH-64 в конце первого квартала 2017 года после окончательного развертывания в Южной Корее .
На данный момент он все еще находится в эксплуатации в нескольких странах, включая Саудовскую Аравию (новые самолеты), Хорватию и Тунис (в которых американские самолеты были выведены из эксплуатации).
Armement
OH-58D «Guerrier Kiowa»
La configuration de l’arme est généralement choisie pour qu’une équipe de deux hélicoptères porte un mélange d’armes possibles. Le 17e escadron de cavalerie du 1er escadron de l’armée américaine aurait environ 15 guerriers Kiowa dans une version à faible observation . A cet effet, les machines ont été revêtues de matériaux absorbant le radar pour réduire la section transversale du radar .
- Charge utile jusqu’à 907 kg sur deux bâtis de charge externes
- Missile guidé air-air
2 lanceurs de missiles à double guidage ATAS (Air To Air Stinger) pour 2 blocs RMP Raytheon AIM-92 «Stinger» I chacun — commandés par infrarouge pour de courtes distances
- Missiles air-sol non guidés
- 2 conteneurs de lancement de tube de fusée LAU-260 / A pour 7 fusées air-sol Hydra non guidées chacun ; Calibre 68 mm / 2,75 pouces
- 2 × conteneurs de lancement de tube de fusée LAU-68D / A pour 7 × fusées hydra air-sol FFAR non guidées chacun; Calibre 70 mm
- 2 × LAU-131 / A conteneurs de lancement de tube de fusée pour 7 × hydra-roquettes air-sol FFAR non guidées chacun; Calibre 70 mm
- Missiles guidés air-sol ( missiles guidés antichar )
2 × suspensions de missiles guidés M299 pour 2 × Boeing Corp / Martin Marietta AGM-114F / N «Hellfire» — commandées par laser
- Canon externe
- 2 × systèmes d’armes M-27 composés chacun de 1 × 7,62 mm mitrailleuse Gatling General Electric M134 avec 2000 cartouches chacun
- 2 mitrailleuses Browning M296 de 12,7 mm avec 500 cartouches chacune
- 2 mitrailleuses Gatling 12,7 mm à trois canons General Dynamics GECAL 50 ( GAU-19 / A) avec 2000 cartouches chacune (cadence: 2000 ou 4000 coups / min; portée jusqu’à 1000 m)
Технические характеристики Bell OH-58 Kiowa.
- Экипаж: 2 человека;
- Вместимость: 4 человека (В зависимости от модификации);
- Длина вертолёта: 9,8 м. (В зависимости от модификации);
- Высота вертолёта: 2,92 м. (В зависимости от модификации);
- Диаметр несущего винта: 10,78 м. (В зависимости от модификации);
- Масса пустого вертолёта: 718 кг. (В зависимости от модификации);
- Максимальный взлётный вес: 1360 кг. (В зависимости от модификации);
- Крейсерская скорость: 190 км\ч. (В зависимости от модификации);
- Максимальная скорость полёта: 220 км\ч. (В зависимости от модификации);
- Максимальная дальность полёта: 480 км. (В зависимости от модификации);
- Максимальная высота полёта: 5800 м.;
- Силовая установка: Allison T63-A-700 (В зависимости от модификации);
- Мощность: 317 л.с. (В зависимости от модификации).
Посмотреть другие вертолеты
Подписывайтесь на актуальные новости
Добавить комментарий
«Бич» UC-43/GB-2 «Трэвеллер». Фото. Характеристики.
XMobots Apoena. Технические характеристики. Фото.
Лучшие места салона самолета A320-200 — Air Astana
Последние новости:
Российская противоспутниковая ракета «Контакт» перепугала Запад
В США объявили о создании гиперзвуковой ракеты, которая летит со скоростью больше 80 МАХ
Россия перебрасывает в Сирию шесть истребителей МиГ-29
Последнее видео:
День Победы 9 мая 2020 75-я годовщина Победы! Парад 1945 / Обращение президента / Бессмертный полк
Полёт российских перехватчиков МиГ-31 на малой высоте
Пустая Москва / Карантин / Видео
Далее
Hydra-70 Family
In the following, the nine main variants of the Hydra-70 rocket are presented:
M151 High-Explosive:
The M151 HEPD is a unitary fragmenting 10-pound anti-personnel, anti-material warhead with the M423 Point Detonating Fuze. Upon detonation, the warhead fragments into thousands of small high velocity fragments. The fuzed warhead is 16.2″ long and weighs 9.3 pounds.
M156:
The M156 white phosphorus (smoke) is primarily used for target marking. The M156 has the same ballistic characteristics as the M151 warhead and is of similar construction. Filler for the M156 is 2.2 pounds of white phosphorus with a 0.12 pound bursting charge of composition B. The fuzed warhead is 16.2″ long and weighs 9.65 pounds.
M229 High Explosive:
The M229 High Explosive warhead is a heavier version of the M151. The U.S. Army is currently not buying this variant. The fuzed warhead is 26″ long and weighs 17 pounds.

82nd Combat Aviation Brigade / Photo by Sgt. 1st Class Eric Pahon
M255A1 Flechette:
The M255A1 Flechette warhead consists of a nose cone assembly, a warhead case, an integral fuze, 1,179 60-grain flechettes and an expulsion charge assembly. The primary fuze (M439) is remotely set with the Aerial Rocket Control System (ARCS) Multifunctional Display (MFD) or Rocket Management System (RMS) to provide a range from 500 meters to 7,200 meters. At expulsion, the 1,179 60-grain, hardened-steel flechettes separate and form a disk-like mass which breaks up with each flechette assuming an independent trajectory. The flechette uses kinetic energy derived from the velocity of the rocket to produce the desired impact and penetration of the target. The fuzed warhead is 26.9″ long and weighs 14 pounds.
M257 Illuminating Flare:
The M257 Illuminating warhead is designed to provide battlefield illumination and does not require the use of Infrared (IR) goggles. The M257 flare rocket can be launched by from either fixed wing or rotary-wing aircraft. The M442 motor burnout fuze functions after a 9-second delay. The fuzed warhead is 29.1″ long and weighs 11 pounds.

101st Combat Aviation Brigade / Photo by Staff Sgt. Ryan Matson
M261 Multi-Purpose Submunition (MPSM):
The MPSM warhead (weight is 13.9 pounds) provides improved lethal effectiveness against area targets such as light armor, wheeled vehicles, materiel, and personnel. The M73 Submunitions are deployed over the target and descend almost vertically. The M261 Warhead is a cargo warhead consisting of a nose cone assembly, a case, integral fuze, nine submunitions, and an expulsion charge assembly. The primary M439 warhead fuze is remotely set with the Aerial Rocket Control System (ARCS), Multifunctional Display (MFD) or Rocket Management System (RMS) to provide a range from 500 meters to 7,200 meters.
M264 RP Smoke:
The M264 RP (red phosphorous) Smoke is used as a red phosphorous filled smoke rocket propelled by the Mk 66 motor and the smoke is deployed at a range set remotely from within the aircraft cockpit. The M264 warhead is used for smoke obscuration in the visible light spectrum. The fuzed warhead is 26.9″ long and weighs 8.6 pounds.
M274 Smoke Signature (practice):
The M274 warhead is a smoke/flash signature practice warhead used for pilot/gunner training missions and consists of a cast iron warhead modified with vent holes, an aluminum nose cap with firing pin, a M423 fuze safe and arming device, and a smoke/flash cartridge. The fuzed warhead is 16.2″ long and weighs 9.3 pounds.
M278 Infrared Flare:
The M278 Infrared Flare warhead is designed for battlefield illumination for use with Infrared (IR) goggles. The flare rockets can be launched from either fixed wing or rotary-wing aircraft. The 442 motor burnout fuze functions after a 9-second delay. The fuzed warhead is 29.1″ long and weighs 11 pounds.
WTU-1/B (practice):
The fuzed warhead is 16.2″ long and weighs 9.3 pounds.
Source fi-aeroweb.com
2.75-inch/70mm DAGR missile
The 2.75-inch/70mm DAGR missile is a precision-strike, multi-role, multi-platform munition that effectively neutralizes lightly-armored and high-value targets close to civilian assets or friendly forces. DAGR offers strike capability with the reliability of a HELLFIRE II missile while further limiting collateral damage.
The DAGR system puts HELLFIRE II missile and Joint Air-to-Ground Missile technology in a 2.75-inch guidance section that integrates seamlessly with legacy Hydra-70 rockets. Like HELLFIRE, DAGR offers lock-on-after-launch (LOAL) and lock-on-before-launch (LOBL) capability, target handoff, enhanced built-in testing on the rail, and laser coding from the cockpit. The result is a laser-guided missile that offers capabilities beyond those of a simple guided rocket.
The DAGR rail-mounted canister (RMC) mounts to HELLFIRE-compatible digital and analog launchers (e.g., M299/M310 and M272). The RMC readily integrates with all HELLFIRE platforms, including unmanned aerial vehicles and Apache, Kiowa, Little Bird, Cobra, and Tiger helicopters.
Plug-and-play HELLFIRE II compatibility allows aircrews to mix loadouts between HELLFIRE and DAGR missiles on the same launcher, providing the flexibility to meet any challenge on an ever-changing battlefield. When increased loadout or reduced weight is a must, DAGR delivers. Source lockheedmartin.com
Mission processors control the suite of mission subsystems via a military standard 1553B bus. An onboard computer provides laser ranging and target location within 10m.
Countermeasures

55th Signal Company (Combat Camera) / Photo by Spc. Kristina Truluck
The countermeasures suite includes an AN/ALQ-144 infrared jammer, radar warning receivers against pulsed and continuous wave radars and a laser warning detector.
Self-defence: AN/APR-39(V)1 or -39A(V)1 RWR. Phase 1 adds AN/ALQ-144 IR jammer, second RWR (AN/APR-44(V)3) and AN/AVR-2 laser detection system. Source aviastar.org
succesor
Deoarece au existat pierderi mari în Irak și elicopterele, dintre care unele au aproape 40 de ani, ajung încet la sfârșitul duratei lor de viață, elicopterul de recunoaștere armată (ARH) a fost scos la licitație pe 9 decembrie 2004 . Elicopterul Bell Textron a participat cu elicopterele Bell 407 , MD, totuși, cu un pasăre MH-6 modernizat . La 29 iulie 2005, armata Statelor Unite a anunțat Bell 407 ca câștigător al licitației ARH. Elicopterul bazat pe Bell 407 a fost numit acum ARH-70A și urma să înlocuiască vechile mașini Kiowa din 2008, cu achiziționarea a 368 de elicoptere planificate. Cu toate acestea, la 16 octombrie 2008, Pentagonul a anunțat că va opri achiziția ARH-70. Motivul pentru aceasta a fost performanța insuficientă și faptul că s-au depășit costurile de achiziție.
EADS oferă Armatei Statelor Unite un succesor, Armed Scout 645 , care se află în prezent în faza de dezvoltare și demonstrație. Între timp, există încercări de a dota elicopterele existente cu noi instrumente de pilotaj din sticlă ; faza de ofertă este așteptată pentru 2011.
În mai 2014, armata Statelor Unite a început reducerea flotei Kiowa . Elicopterele scoase din funcțiune vor fi oferite spre vânzare altor forțe armate.
Utilisateurs
Peinture spéciale OH-58B
Armée fédérale OH-58
Australie Royal Australian Air Force / Royal Australian Navy
- 56 × OH-58A «Kiowa»
- Après la livraison de 12 hélicoptères, les 44 autres ont été construits sous licence CAC CA-32 et mis hors service en 2000. Ils ont été remplacés aujourd’hui par l’Eurocopter Tiger ARH.
République Dominicaine Force aérienne dominicaine / Fuerza Aérea Dominicana
- 10 x OH-58A / C «Kiowa».
Grèce Grèce
- 70 × COH-58D «Kiowa» (spécimens utilisés par l’armée américaine, dont 36 hélicoptères d’urgence et 10 hélicoptères scolaires, le reste servant de magasin de pièces détachées)
Israël Israël
- 12 × OH-58B «Kiowa».
Canada Forces canadiennes
- 0 × COH-58A / CH-136 «Kiowa» (74 exploités et mis hors service)
Croatie Croate Air Force / Oružane snage Republike Hrvatske
- 16 × OH-58D «Kiowa»
L’Autriche Force aérienne (armée fédérale)
- 12 × OH-58B «Kiowa»
- À partir de 1978, 300 OH-58A ont été convertis en la version plus puissante OH-58C (les OH-58B étaient des modèles pour l’exportation vers l’Autriche). Les premiers OH-58B pour l’Autriche ont été livrés à Langenlebarn le 14 juin 1976 (3C-OA à 3C-OF) dans des boîtes, partiellement assemblées .
Taïwan Armée de la République de Chine
- 39 × OH-58D «Kiowa»
Tunisie Forces armées tunisiennes
- 24 × OH-58D «Kiowa»
Arabie Saoudite Force aérienne royale saoudienne
- étaient 15 × Bell 406CS «Combat Scout»
États Unis Armée des États-Unis
- environ 2000 x OH-58A / C / D
Stationné en Allemagne et en Autriche
Outre les «Kiowas» autrichiens, les hélicoptères étaient également stationnés sur un certain nombre de bases américaines dans le sud de l’Allemagne, comme l’ aérodrome de l’armée Maurice Rose à Francfort-Bonames ou l’héliport de Büdingen (deux unités purement OH-58) et sur la BFC Lahr .







